42.filter
PR #906
Watch improvements.
/*
Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
*/
package watch
import ()
// FilterFunc should take an event, possibly modify it in some way, and return
// the modified event. If the event should be ignored, then return keep=false.
type FilterFunc func(in Event) (out Event, keep bool)
// Filter passes all events through f before allowing them to pass on.
// Putting a filter on a watch, as an unavoidable side-effect due to the way
// go channels work, effectively causes the watch's event channel to have its
// queue length increased by one.
func Filter(w Interface, f FilterFunc) Interface {
fw := &filteredWatch{
incoming: w,
result: make(chan Event),
f: f,
}
go fw.loop()
return fw
}
type filteredWatch struct {
incoming Interface
result chan Event
f FilterFunc
}
// ResultChan returns a channel which will receive filtered events.
func (fw *filteredWatch) ResultChan() <-chan Event {
return fw.result
}
// Stop stops the upstream watch, which will eventually stop this watch.
func (fw *filteredWatch) Stop() {
fw.incoming.Stop()
}
// loop waits for new values, filters them, and resends them.
func (fw *filteredWatch) loop() {
defer close(fw.result)
for {
event, ok := <-fw.incoming.ResultChan()
if !ok {
break
}
filtered, keep := fw.f(event)
if keep {
fw.result <- filtered
}
}
}

这段代码定义了一个"过滤器"(filter)功能,该功能可对从 watch 接口发出的事件进行处理和筛选。我们从上到下逐步解读下这段代码:
首先,FilterFunc 是一个函数类型,其输入是一个 Event(事件),输出是一个经过可能修改的 Event,以及一个布尔值,表示是否保留该事件。
然后,函数 Filter 创建一个新的 filteredWatch 实例,此实例从输入的 watch 接口接收事件,通过指定的 FilterFunc 进行过滤,然后将结果发送到新的通道。
filteredWatch 是一个结构体,包含了一个输入的 watch 接口,一个结果的通道,以及一个过滤函数。
函数 ResultChan 返回一个可以接收过滤事件的通道。
Stop 函数则会停止上游的 watch,从而最终停止这个 watch。
loop 函数是过滤器的主体,它会持续等待新的事件,过滤它们,然后将保留的事件重新发送。当上游的 watch 停止发出事件时,loop 函数将会结束,并关闭结果通道。
总的来说,这段代码提供了一种机制,可以在接收到事件后进行某种处理或筛选,然后将处理后的事件发送到另一个通道,以供后续处理。这对于需要在接收事件后进行某种预处理的情况非常有用。
PR #913
Allow kubecfg to print custom types
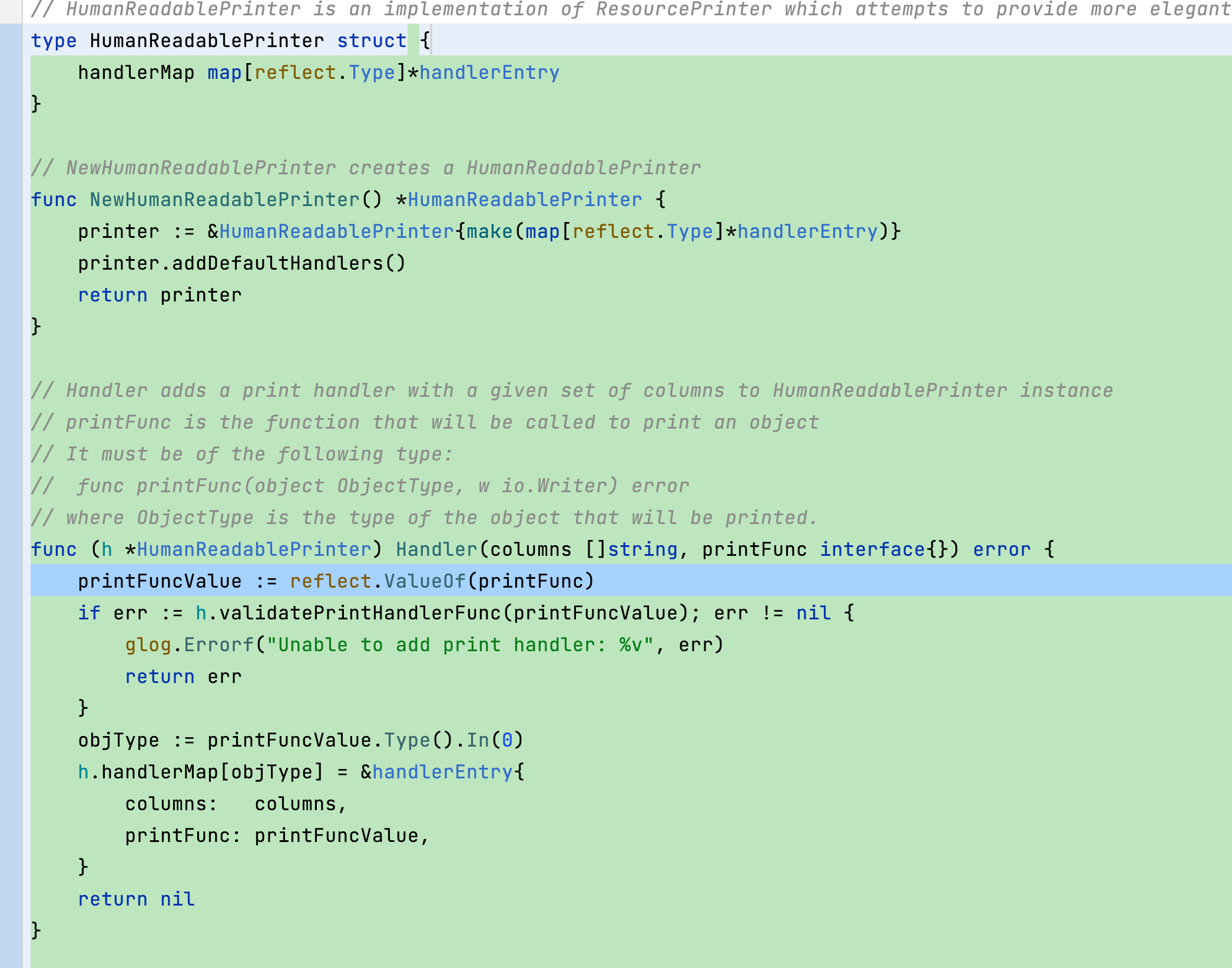
首先,Handler函数接收两个参数:columns,是一个字符串切片,表示要打印的列;printFunc,是一个函数,其作用是打印对象。printFunc必须具有以下类型:
go Copy code func printFunc(object ObjectType, w io.Writer) error 其中,ObjectType是将要打印的对象的类型。
然后,Handler函数获取了printFunc函数的反射值,并验证了这个函数是否符合预期的格式(即是否符合上面提到的printFunc类型)。如果不符合预期,Handler函数将记录错误信息,并返回这个错误。
接着,Handler函数获取了printFunc的输入参数类型,即要打印的对象的类型。
最后,Handler函数将一个包含columns和printFunc的handlerEntry添加到h.handlerMap中,键为对象的类型。如果成功添加,Handler函数返回nil表示没有错误。
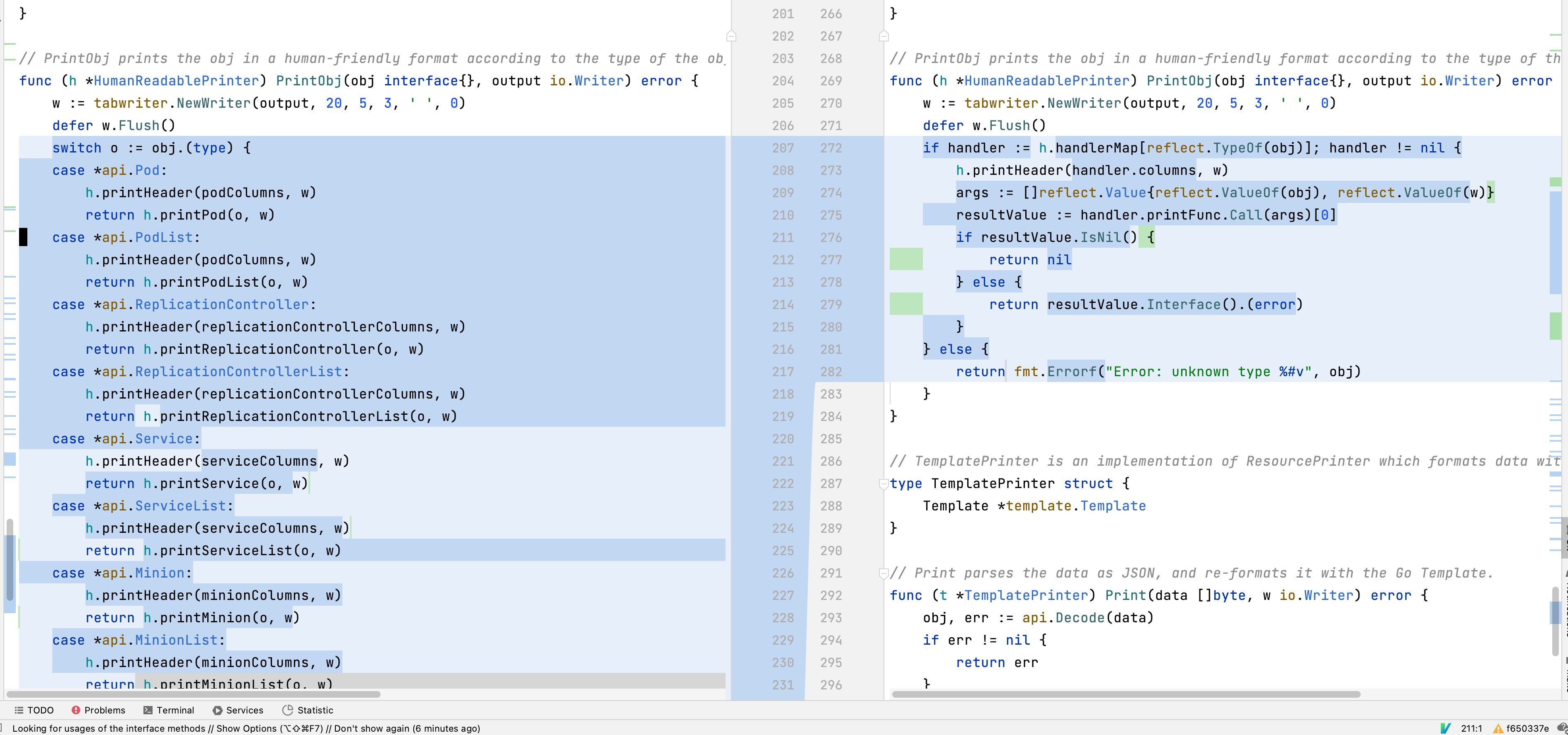
这段代码定义了一个名为 PrintObj 的函数,该函数的目标是根据对象的类型以人类可读的格式打印对象。这段代码涉及的主要是 Go 的反射(reflection)功能。
我们逐行解析这段代码:
首先,PrintObj 函数接受两个参数:obj,是任意类型,代表需要打印的对象;output,是一个 io.Writer 对象,对象打印的输出将写入这个 io.Writer。
然后,使用 tabwriter.NewWriter 创建一个新的 tabwriter.Writer,它将会将输出格式化为表格形式,然后写入 output。
之后,函数查找 handlerMap 中是否存在一个处理程序用于处理传入对象的类型。如果找到,则调用这个处理程序打印对象;如果没有找到,返回一个包含错误信息的 error。
如果找到了合适的处理程序,函数首先打印表格的标题,然后调用处理程序的 printFunc 函数打印对象。调用 printFunc 函数时,需要将对象和 tabwriter.Writer 作为参数。printFunc 函数的返回值是一个 error 类型的反射值,函数检查这个错误是否为 nil,如果不是 nil,则返回这个错误。
总的来说,PrintObj 函数的作用是根据传入的对象类型,找到对应的处理程序,并调用这个处理程序的 printFunc 函数打印对象。如果没有找到对应的处理程序,函数将返回一个错误。
作业
学习理解Go 的反射(reflection)功能。 请实现下面代码中的AddPrintFunc和Print函数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type Pod struct {
ID string
Host string
}
type Service struct {
ID string
Label string
}
func printPod(pod *Pod) error {
fmt.Printf("%s\t%s\t\n", pod.ID, pod.Host)
return nil
}
func printService(svc *Service) error {
fmt.Printf("%s\t%s\t\n", svc.ID, svc.Label)
return nil
}
type handlerEntry struct {
printFunc reflect.Value
}
type HumanReadablePrinter struct {
handlerMap map[reflect.Type]*handlerEntry
}
// 创建printer
func NewHumanReadablePrinter() *HumanReadablePrinter {
printer := &HumanReadablePrinter{
handlerMap: make(map[reflect.Type]*handlerEntry),
}
//添加打印处理函数
printer.addDefaultHandlers()
return printer
}
// 添加默认打印处理函数
func (h *HumanReadablePrinter) addDefaultHandlers() {
h.AddPrintFunc(printPod)
h.AddPrintFunc(printService)
}
// 请实现基于添加对应类型的打印函数,类型从 打印函数的第一个参数获取
func (h *HumanReadablePrinter) AddPrintFunc(printFunc interface{}) error {
//to do
return nil
}
// 请实现基于 reflect的打印函数
func (h *HumanReadablePrinter) Print(obj interface{}) error {
//to do
return nil
}
func main() {
pod := Pod{
ID: "pod1",
Host: "127.0.0.1",
}
svc := Service{
ID: "svc",
Label: "svc-pod1",
}
fmt.Println("type:", reflect.TypeOf(&pod))
fmt.Println("value :", reflect.ValueOf(&pod))
fmt.Println("value elem:", reflect.ValueOf(&pod).Elem())
printer := NewHumanReadablePrinter()
printer.Print(&pod)
printer.Print(&svc)
fmt.Printf("over")
}